In this article
What Is NTFS File System
The Windows NT operating system employs the NT file system (NTFS), also known as the New Technology File System, to store, arrange, and locate files on a hard drive effectively. One kind of file system is NTFS. Both OS as well as the type of disk they are operating with are typically utilized to distinguish between different file systems. Today, files can also be saved across numerous servers using a distributed file system (DFS), which allows for the same access and management as if the files were kept locally. A DFS offers redundancy and makes it simple for several users to exchange data and files over a network.
As part of the 1993 Windows NT 3.1 release, NTFS was originally released.
What Is NTFS File System Used For
NTFS is primarily utilized by the Windows Server range of operating systems.
Windows 10
On Windows Server 2019 and newer, as well as Windows 10, version 1709 and newer, NTFS can support volumes up to 8 petabytes in size (older versions support up to 256 TB). Cluster size and cluster count have an impact on supported volume sizes.
Windows 8
Microsoft is addressing the tablet market with Windows 8. With dedicated touch screen programs and an enhanced user interface, Windows 8 delivers a wealth of new features. One can make the changeover right now with the aid of our many suggestions.
Windows 7
The most reliable and secure file system for Windows 7 is called NTFS, which stands for NT File System. By offering network access and ownership privileges, which allows you to regulate who has access to which files, it offers security.
Windows Vista
Microsoft created the Windows Vista operating system family to be used on personal computers, such as home and office desktops, laptops, tablets, and media center PCs. Windows Deployment Services, SCCM, and Windows Update
Windows XP
Computers running Windows XP are preconfigured with NTFS by default.Users can only utilize crucial functions like Active Directory and copyright security by selecting NTFS as their file system. It is simple to upgrade the partition towards the latest iteration of NTFS using the NTFS setup application.
Windows 2000
A newer version of NTFS, compared to Windows NT 4.0, is included with Windows 2000, and it supports a number of features, including Active Directory. Computers running Windows 2000 are preconfigured with NTFS by default.
Windows NT
The native file system for Windows NT is called NTFS, and it can handle long filenames while also producing short filenames for DOS and 16-bit Windows software. NTFS offers per-file compression and fully implements the NT security model.
The data file on a disk or storage drive is typically created and maintained by a computer OS. The data is organized into files by the file system. It determines the names, locations, updates, and retrieval of data files. The operating system makes a distinction between both the system files and the drive type they are utilized with. There seems to be a distributed file system (DFS) wherein files are handled locally, stored, and stored across numerous servers. DFS offers crucial redundancy and enables many users to exchange data and files on a network.
How Does NTFS Work
Performance, dependability, and compatibility are all features offered by that of the Windows NT file system (NTFS) that are absent from the FAT file system. On very big hard disks, it can quickly carry out basic operations like reading, writing, and searching as well as more complex ones like file-system recovery.
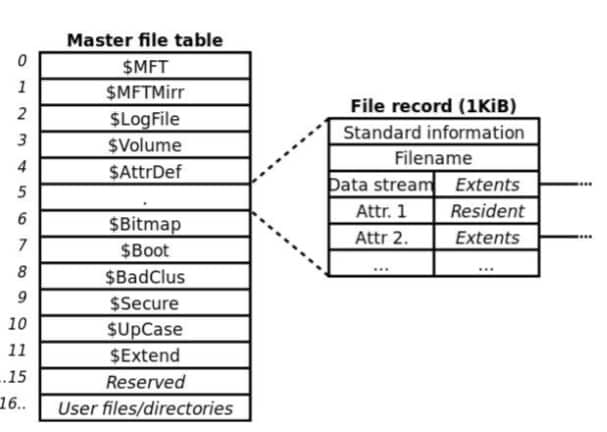
The Master File Table (MFT), which holds data about all of the files and folders on the NTFS disk, is created when a volume is formatted with the NTFS file system, along with numerous other system files.
The structure of an NTFS drive once formatting is complete is shown in the accompanying figure.
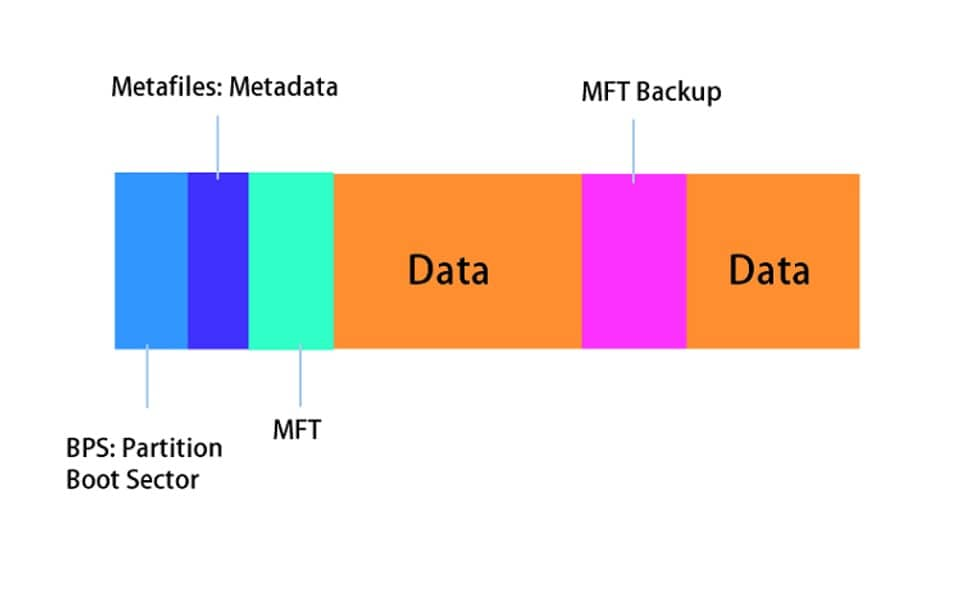
For more details on NTFS, see to the following sections:
Additional datasets that precede the BPB on NTFS disks create an expanded BPB. Ntldr (the NT loader program) can locate the customer master table (MFT) on startup thanks to the information in these fields. In contrast to FAT16 and FAT32 volumes, NTFS volumes do not have a designated sector where the MFT is placed.
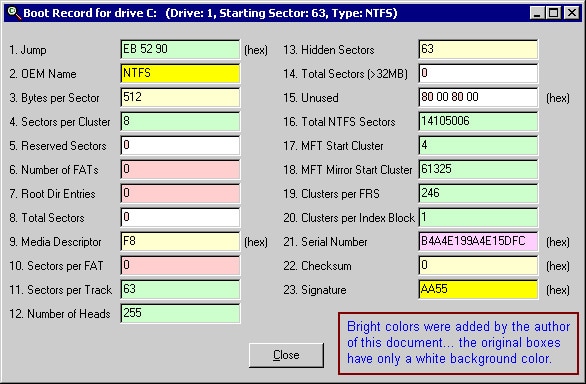
Due to this, if a faulty sector is present in the MFT's usual place, it can be shifted. Windows NT/2000, however, thinks that the drive has never been formatted if indeed the information has been corrupted or even the MFT cannot be found.
A master file table is a unique file that contains records for every file on an NTFS drive (MFT). The table's first 16 records are set aside by NTFS for special data. This table's first results of this investigation showed the master file table in detail, followed by an entry for the MFT mirror.
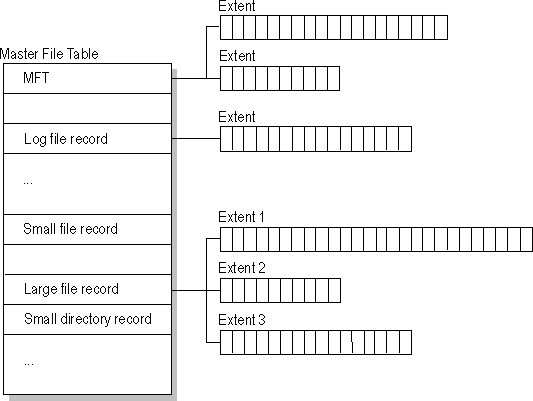
NTFS scans the second record to locate the MFT mirror file, in which the first track is equivalent to the first record of the MFT, if the initial MFT record is corrupted. The boot sector stores the coordinates of the data segments for the MFT and MFT mirror files. The conceptual core of the disk contains a copy of the boot sector.
Most NTFS files are part of Microsoft's New Technology File System. The following list of NTFS file formats is provided:
NTFS File Attributes
Every file (or folder) is seen by the NTFS file system as a collection of file attributes. File properties include things like the file's name, security details, and even data. An attribute type code and, if present, an attribute name serves to identify each attribute. Residents attributes are those of a file that can reside only within an MFT file record. For instance, the MFT file record always contains details like the filename and time stamp. Some of a file's properties are nonresident if all of its data is too vast to accommodate in the MFT file record.
Several system files are part of NTFS, and they are all hidden on the NTFS drive. Any system file is the one that the file system uses to establish the file system and store its metadata. The Format tool writes system files to the volume.
Multiple data streams are supported by NTFS, and each stream name corresponds to a variety of data features on the file. Each data stream has a handle that can be accessed. Therefore, a data stream is a distinct collection of file properties. Streams share rights but have distinct proactive locks, document locks, and sizes.
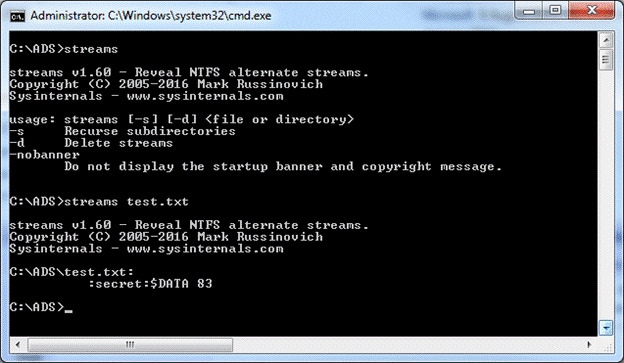
Users are capable of handling information as a single entity thanks to this functionality. An illustration of an alternative stream is as follows:
- dat:stream2
There might be a collection of files defined as different streams, like in the following illustration:
- library:file1
- :file2
- :file3
A file may be linked to multiple programs at once, including Microsoft Word and Microsoft WordPad. For example, the following file structure shows file association but still not multiple files:
- program:source_file
- :doc_file
- :object_file
- :executable_file
There at command prompt, enter commands like the following to generate an alternative data stream:
- echo text>program:source_file
- more < program:source_file
Compression is supported by Windows NT on a per-file, per-folder, and per-NTFS volume level. Any Windows-based application can read and write compressed files on an NTFS disk without needing to first decompress them. The file is automatically decompressed when it is read. When a file is closed or saved, it is once more compressed. In Windows Explorer, compacted folders and files have the attribute C.
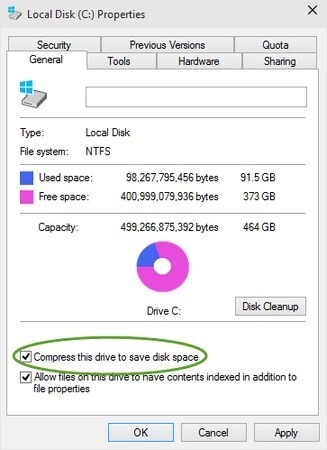
Data in its compressed form can only be read by NTFS. This compression filtration driver defragments the file prior making it accessible when an application like Microsoft® Word or even a windows os command like copy asks access to the file.
The primary file encryption mechanism for storing encrypted files on NTFS drives is provided by the Encrypting File System (EFS). EFS protects files from others who could get unlawful physical access to sensitive data that is being stored.
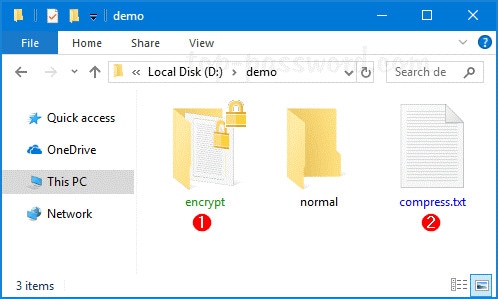
EFS combines public key technology along with symmetric key encryption to safeguard files and guarantee that solely the holder of a document can access it. A digital certificate containing a public as well as a private key pair is given to EFS users. When a user is logged in to the user's machine in which the cryptographic signature is kept, EFS utilizes whatever key set for that user.
A property of a sparse file forces the I/O system to generate only useful (nonzero) data. Non-meaningful data (long strings of zero-filled data) is not allocated on disk; only non-zero data is. Authorized data is returned in the same form as it was stored whenever a sparse file is read; non-allocated data is by default returned as zeros.
Sparse data streams are dealt with by NTFS, which only keeps other data in its allotted state. The file system returns allotted data as real data and deallocated information as zeros when a program reads a sparse file.
Data Integrity and Recoverability with NTFS
The consistency of the volume is ensured by the recoverable file system NTFS by employing conventional transactional logging and recovery procedures. When a disk fails, NTFS performs a recovery process that consults data kept in a log file in order to restore consistency.
The precise nature of the NTFS recovery process ensures that the volume is returned to a valid state. Very little overhead is required for transaction logging. The very first moment a software accesses an NTFS volume once the computer is restarted after a failure, NTFS automatically performs disk recovery operations to ensure the security of all NTFS volumes.
Features of NTFS File System
The fact that NTFS supports file permissions and encryption, as opposed to FAT, is one way in which it differs from the latter. NTFS has the following notable features:
Organizational Potency
The b-tree directory structure is used by NTFS to manage file clusters. This is crucial because it enables effective file structure and sorting.
Accessible Data
It stores information about such a file's cluster centers as well as other information in the MFT instead of just in a cumulative governing table like FAT.
Data Volume
Large files can be supported using NTFS.
User Permissions
A server administrator can control who has access to particular files using the access control list it has.
Compression
Integrated file compression reduces file sizes and increases storage space.
Unicode File Naming
NTFS provides a more logical file naming system and permits extended file names with a greater variety of characters because it enables system files based on Unicode. Sometimes translation is needed for naming standards that aren't Unicode.
Security
Data on both transportable and non-removable disks is secure thanks to NTFS.
Requires Less Storage
It includes assistance for sparse records that substitutes empty information — long sequences of zeros — with information that consumes up a lesser volume of storage capacity.
Easy Access to Volume
Disk partitions can be managed as regular directories throughout the file system thanks to NTFS's use of mounted volumes.
Pros and Cons of NTFS File System
The following list of NTFS's pros and cons contains more information.
Pros:
Control
Disk quotas, which provide businesses broader control over storage space, are one of the main characteristics of NTFS. Disk quotas can be used by administrators to restrict a certain user's access to a certain amount of storage space.
Performance
NTFS utilizes file compression to reduce file sizes, boost file transfer rates, and provide organizations with extra storage capacity. Additionally, it accepts very huge files.
Security
Administrators can set rights on sensitive data using NTFS's access control features to limit access to specific users. Encryption is supported as well.
Easy Logging
Operators can monitor files that have recently been added, removed, or altered in any way thanks to the MFT's logging and auditing of the drive's data. NTFS logs occurrences in such a file system log since it is a tracking file system.
Reliability
Since NTFS keeps the coherence of the file system, information and files can be promptly recovered in the event that the system fails or malfunction. It includes an MFT mirrored file which the system can turn to if the original MFT becomes corrupt because it is a fault-tolerant system.
Cons:
OS Compatibility Issues
NTFS's limited OS compatibility—it can only be read on non-Windows OSes—is its biggest drawback.
Limited Support for Devices
Many portable devices, such as Android smartphones, DVD players, and digital cameras, do not support NTFS. Other gadgets like media players, smart TVs, and printers don't support it either.
Mac OS X Assistance
NTFS disks are only partially compatible with OS X devices; they can be read from but not written to.
NTFS Alternatives
FAT32 is the earliest of the three file systems since it was created by Microsoft before NTFS. It is typically thought to be less effective than NTFS. It has 32 GB volumes in Windows and a lower 4 GB file size. Each of NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT has advantages and disadvantages.
They are all utilized in a range of computing scenarios, ranging from personal to business. NTFS is the most well-known of the three due to its association with Windows.
The table below lists some key distinctions between the NTFS File System, exFAT, and FAT32 file systems:
|
NTFS |
FAT32 |
exFAT |
|
It gained popularity after Windows XP, although NTFS debuted with Windows NT |
The FAT32 file system was initially made available with Windows 95. |
Windows XP and Vista operating systems introduced exFAT. |
|
File permissions, backup shadow copies, encryption, disk quota restrictions, etc. are all supported by NTFS |
Quickly accessible and simple to use format. |
Flash drives work well with it. |
|
Suitable with all Windows versions |
With every Windows version, it functions flawlessly. Linux, Mac, etc. |
All Windows versions are compatible with it. |
|
It is read-only on Mac and some Linux versions |
Does not require any extra setup in order to work with Mac devices. |
All editions of Windows and Mac OS X support the exFAT file system, while Linux requires special software. |
|
There are no specific file or partition size limits |
Maximum file sizes are 4 GB and 8 TB, respectively. |
It does not have any specific size of the file or partition size restrictions. |
|
The most recent file system is NTFS. Windows uses NTFS as the system drive and, through default, for the majority of non-removable drives. |
An outdated file system called FAT32 that is less effective than NTFS. |
ExFAT, a more recent alternative to FAT 32 that is supported by more hardware and operating systems than NTFS, is still not as widely used as FAT32. |
Source Link: https://www.guru99.com/fat32-vs-exfat-vs-ntfs-difference.html
The Bottomline
NTFS is a file system used by Microsoft Windows as well as some detachable storage devices to classify, name, and store files. Depending on the device's storage capacity, the OS being used, or the kind of drive, a separate file system, like FAT32 or Extended FAT, may be preferred (exFAT). Every file system has advantages and disadvantages. For instance, NTFS offers more sophisticated security and rights than exFAT and FAT32. FAT32 and exFAT, on the contrary hand, perform better with operating systems other than Windows, such Mac and Linux.








